HR Analytics Overview: Absenteeism Project
Requirements from HR departments
- Provide a list of Healthy Individuals & Low Absenteeism for the healthy bonus program (Total Budget: $1000 USD)
- Calculate a Wage Increase or annual compensation for Non-Smokers (Insurance Budget: $983,221)
- Create a Dashboard for HR to understand Absenteeism at work based on the approved wireframe.
Employee data can be found in the CSV files located in the my repository here: HR-dataset-project
Project Details
Start by creating a join table to combine all relevant datasets and ensure accurate employee information.
Input [1]:
SELECT *
FROM Absenteeism_at_work a
LEFT JOIN compensation b
ON a.ID = b.ID
LEFT JOIN Reasons c
ON a.Reason_for_absence = c.Number;
Output [1]:
| ID | Reason for absence | Month of absence | Day of the week | Seasons | Transportation expense | Distance from Residence to Work | Service time | Age | Work load Average/day | Hit target | Disciplinary failure | Education | Son | Social drinker | Social smoker | Pet | Weight | Height | Body mass index | Absenteeism time in hours | ID | comp_hr | Number | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 26 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 289 | 36 | 13 | 33 | 239554 | 97 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 90 | 172 | 30 | 4 | 1 | 35 | 26 | unjustified absence |
| 2 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 118 | 13 | 18 | 50 | 239554 | 97 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 98 | 178 | 31 | 0 | 2 | 49 | 0 | Unkown |
| 3 | 23 | 7 | 4 | 1 | 179 | 51 | 18 | 38 | 239554 | 97 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 89 | 170 | 31 | 2 | 3 | 47 | 23 | medical consultation |
| 4 | 7 | 7 | 5 | 1 | 279 | 5 | 14 | 39 | 239554 | 97 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 68 | 168 | 24 | 4 | 4 | 51 | 7 | Diseases of the eye and adnexa |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 737 | 11 | 7 | 3 | 1 | 235 | 11 | 14 | 37 | 264604 | 93 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 88 | 172 | 29 | 4 | 737 | 26 | 11 | Diseases of the digestive system |
| 738 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 118 | 14 | 13 | 40 | 271219 | 95 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 98 | 170 | 34 | 0 | 738 | 48 | 0 | Unknown |
| 739 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 2 | 231 | 35 | 14 | 39 | 271219 | 95 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 100 | 170 | 35 | 0 | 739 | 42 | 0 | Unknown |
| 740 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 3 | 179 | 45 | 14 | 53 | 271219 | 95 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 77 | 175 | 25 | 0 | 740 | 55 | 0 | Unknown |
From this, we find the list of employees who are healthy individuals and have low absenteeism for the bonus program. With the assumption that healthy individuals are non-smokers and non-drinkers, their BMI is less than 25, and their absence time must be under the average of the list.
Input [2]:
SELECT * FROM Absenteeism_at_work a
LEFT JOIN compensation b
ON a.ID = b.ID
LEFT JOIN Reasons c
ON a.Reason_for_absence = c.Number
WHERE Social_drinker = 0
AND Social_smoker = 0
AND Body_mass_index < 25
AND Absenteeism_time_in_hours < (SELECT AVG(Absenteeism_time_in_hours) FROM Absenteeism_at_work)
ORDER BY Absenteeism_time_in_hours;
Output [2]:
| # | ID | Reason for absence | Month of absence | Day of the week | Seasons | Transportation expense | Distance from Residence to Work | Service time | Age | Work load Average/day | Hit target | Disciplinary failure | Education | Son | Social drinker | Social smoker | Pet | Weight | Height | Body mass index | Absenteeism time in hours | ID | comp_hr | Number | Reason |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 52 | 0 | 9 | 2 | 4 | 225 | 26 | 9 | 28 | 241476 | 92 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 69 | 169 | 24 | 0 | 52 | 42 | 0 | Unknown |
| 2 | 217 | 0 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 388 | 15 | 9 | 50 | 378884 | 92 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 76 | 178 | 24 | 0 | 217 | 42 | 0 | Unknown |
| 3 | 531 | 0 | 10 | 2 | 4 | 225 | 26 | 9 | 28 | 284853 | 91 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 69 | 169 | 24 | 0 | 531 | 25 | 0 | Unknown |
| 4 | 559 | 13 | 12 | 6 | 4 | 179 | 26 | 9 | 30 | 280549 | 98 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56 | 171 | 19 | 1 | 559 | 51 | 13 | Diseases of the musculoskeletal system and connective tissue |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 108 | 540 | 23 | 11 | 6 | 4 | 225 | 26 | 9 | 28 | 268519 | 93 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 69 | 169 | 24 | 4 | 540 | 47 | 23 | Medical Consultation |
| 109 | 315 | 1 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 179 | 26 | 9 | 30 | 265017 | 88 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56 | 171 | 19 | 5 | 315 | 47 | 1 | Certain Infectious and Parasitic Diseases |
| 110 | 316 | 7 | 10 | 4 | 4 | 179 | 26 | 9 | 30 | 265017 | 88 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 56 | 171 | 19 | 5 | 316 | 37 | 7 | Diseases of the Eye and Adnexa |
| 111 | 359 | 23 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 225 | 26 | 9 | 28 | 330061 | 100 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 69 | 169 | 24 | 5 | 359 | 49 | 23 | Medical Consultation |
Here we have the list of company employees who have a healthy lifestyle that matches the selection criteria for the bonus program. The output comes with 111 employees.
Requirement 2
Let’s move on to the next requirement from HR: calculating a wage increase or annual compensation for the insurance budget of $983,221 for all non-smokers
Note: the requirement is to calculate a wage increase or annual compensation for the insurance budget of $983,221 for ALL NON-SMOKER, it shall not be the same list as the previous requirement.Firstly, query the number of employees who are nonsmokers:
Input [3]:
SELECT COUNT(*) AS count_nonsmoker
FROM Absenteeism_at_work
WHERE Social_smoker = 0;
Output [3]:
| count_nonsmoker |
|---|
| 686 |
Calculate the total number of hours nonsmokers worked in a year if they worked 8 hours per day, 5 days a week, for 52 weeks: 686 x 8 x 5 x 52 = 1426880 (hours)
Next, calculate how much the hourly wage of a nonsmoker increases as the company's insurance budget increases by $983,221: 983221/1426880 = 0.68907 ($/hour)
Let's do it backward to see the cost in total for an employee per year after the company increases the insurance budget: 0.68907 x 8 x 5 x 52 = 1,433.26 ($/year)
The rise of 0.689 dollar per hour in an employee's hourly income may seem substantial, but a mere $1433 payment for a nonsmoker employee's insurance will have a significant impact on wellness and employee incentives. That's just too tiny for the company to encourage employees to get a better lifestyle for the next bonus program.
Requirement 3
Before creating dashboard sections, as you can see from the two previous requirements, we query the data by using SELECT * all the time, which makes sense for people who just check out for the first time and want complete information. For some columns that we don't need in PowerBI, optimize the query again using:
Input [4]:
SELECT
a.ID,
c.Reason,
a.Month_of_absence,
a.Body_mass_index,
CASE
WHEN a.Body_mass_index < 18.5 THEN 'Underweight'
WHEN a.Body_mass_index BETWEEN 18.5 AND 25 THEN 'Healthy'
WHEN a.Body_mass_index BETWEEN 25 AND 30 THEN 'Overweight'
WHEN a.Body_mass_index > 40 THEN 'Obese'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END AS BMI_Caretory,
CASE
WHEN Month_of_absence IN (12,1,2) THEN 'Winter'
WHEN Month_of_absence IN (3,4,5) THEN 'Spring'
WHEN Month_of_absence IN (6,7,8) THEN 'Summer'
WHEN Month_of_absence IN (9,10,11) THEN 'Fall'
ELSE 'Unknown'
END AS seasons_name,
Seasons,
Month_of_absence,
Day_of_the_week,
Transportation_expense,
Education,
Son,
Social_drinker,
Social_smoker,
Pet,
Disciplinary_failure,
Age,
Work_load_Average_day,
Absenteeism_time_in_hours
FROM Absenteeism_at_work a
LEFT JOIN compensation b
ON a.ID = b.ID
LEFT JOIN Reasons c
ON a.Reason_for_absence = c.Number;
And we will use it to create a dashboard using PowerBI with a frame approved by HR departments here.
The wireframe
And check my final report here in PowerBI.
Insights and Recomendation from the data
Insight 1
By filtering the Count of Reason, it is simple to identify the 4 most common reasons, all of which are related to the employee's health: 385/740, or 52.02%, that employees mentioned when they asked for absence permission.
Furthermore, if we include all the health-related factors, the percentage could be more than 70%, and it has a significant impact on the employee's performance throughout the week, not only at the beginning of the week.
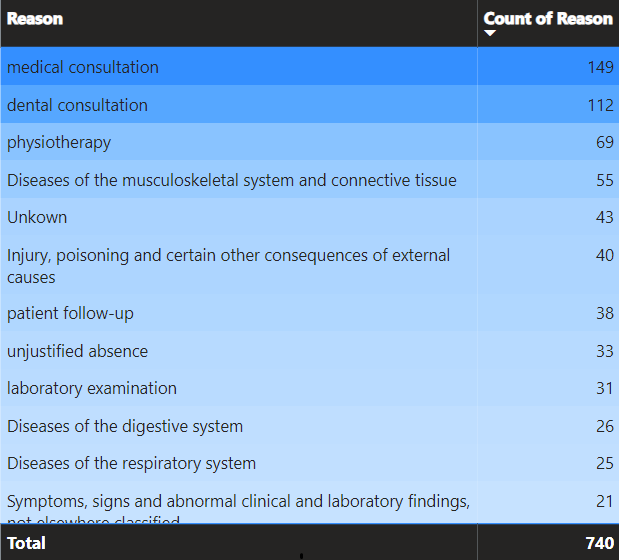
Recomendation:
- For this reason, HR departments pay attention to the employee's health in their workplace and have a plan to provide insurance for employees by analyzing more employee's data to have a specific policy.
Insight 2
As the report shows in the graph of Sum of Absenteeism time in hour by Day of the week, amount of employees's absence time is highest on Monday of the week and decreases steadily until the end of the week. That's a lot of sense in reality, and there are a lot of factors that could have contributed to this, such as employees unfortunately getting into an unexpected situation for their health reasons (Insight 1) where they couldn't go to work at the beginning of the week, or in another scenario, employees may spend much time on their entertainment activities at the previous weekend.
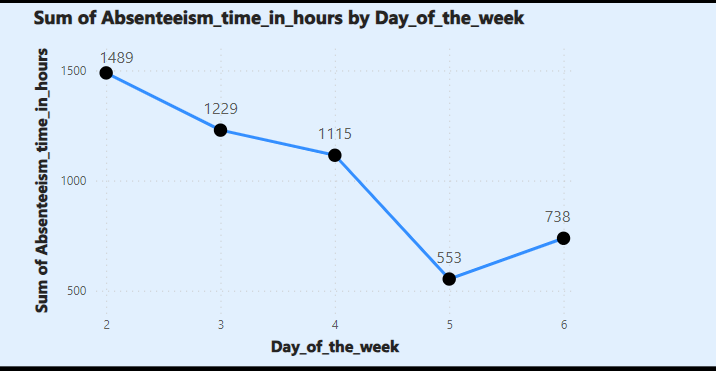
Recomendation:
- Adjusting or reducing the working time to adapt the employee's reality schedule by adjusting from 8 a.m-5 p.m to 10 a.m - 7 p.m or reducing working hours from 8 a.m - 5 p.m to 10 a.m - 5 p.m, will guarantee employees get high performance at the beginning of the week.
- Establishing policies that encourage employees to reduce their absence time at the beginning of the week, like providing more employees's welfare on Monday, Tuesday, and Wednesday.